What is Crypto Staking- How It Works, Benefits, Risks, and Future
Contents
Much value is staked on layer 1s (such as Ethereum, Solana, Cardano, etc.) and layer 2s (such as BNB Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, etc.), as well as decentralized applications (dApps) that run on these platforms.
Without staking, most blockchains and their applications would not function. Staking allows these platforms to remain decentralized while delivering services with an efficiency that matches or exceeds, in some aspects, that of centralized entities.
What is Crypto Staking?
In simple terms, staking refers to allowing a protocol of a blockchain or decentralized app to use the crypto assets in your wallet as some sort of lottery ticket that is used to select the next node on its peer-to-peer network that will update the shared ledger on behalf of everyone else.
The more assets are linked (staked) to a particular node on the network, the more likely it is to be selected to add transactions to the shared ledger or perform any other task that the protocol specifies. In return, it earns rewards.
On some networks, you can’t move the assets from your wallet once you stake them until the period of staking has ended, which can be anything from a few hours to weeks. On others, you receive tokens representing your staked assets, which you can use on other platforms as collateral or even another stake. This is known as liquid staking.
Staking is the primary alternative to the Proof of Work(PoW) consensus mechanism used by the Bitcoin network. Satoshi Nakamoto developed this process to help select nodes (miners) on the peer-to-peer network that update the shared transaction ledger (record).
On the Bitcoin network, mining nodes compete to solve a mathematical problem. This requires compiling transactions and processing them to get a value. The first node to complete this task has its transaction accepted by the others as the new record on the ledger and is rewarded with new coins and the fees paid by users.
This process, known as Proof of Work (PoW), is energy-intensive and requires highly efficient hardware, which can be very costly. The cost of these two critical components deters those who might want to harm the network. Hardly anyone wants to spend significant resources on hardware and energy and not recoup them. Those who act inappropriately on the Bitcoin network are ignored and not rewarded, making their efforts futile.
While proof of work has effectively secured the Bitcoin network and a few others, it has shortcomings. The most prominent are the huge amounts of energy it consumes and the cost of acquiring the necessary hardware.
Because of these shortcomings, blockchain developers have built alternatives to PoW that consume less power and have fewer hardware demands. Proof of Staking (PoS) is the earliest alternative and has become one of the most successfully used. According to several reports, nearly 60% of all blockchains and over 90% of DApps with internal governance structures use PoS as their consensus mechanism.
How Crypto Staking Works
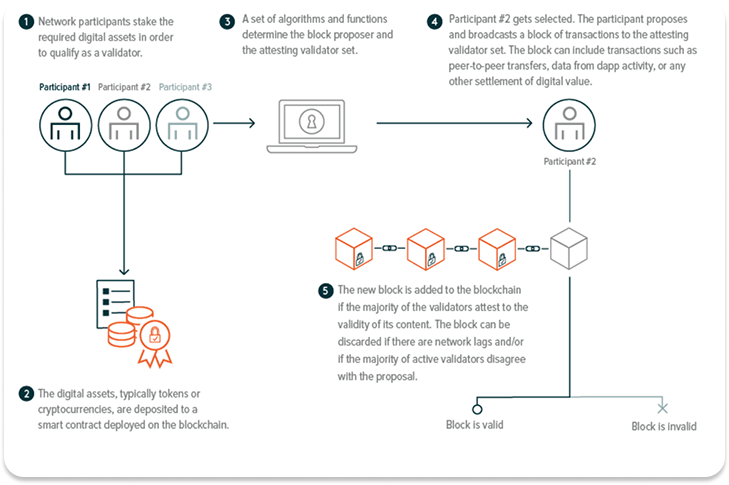
Of course, crypto staking works differently, at least to some extent, on each platform or protocol where it is applied. However, the general process involves finding the protocol you want to stake on, getting the coins you can stake, and giving a node or pool on the network permission to use the assets in your wallet as part of its stake. Usually, there is a user interface for this.
Some protocols lock the assets, while others allow you to get out at any time you want. On others, you are given tokens that represent your staked coins, which you can re-stake or even use as collateral.
It is important to note that you can stake directly on the network or through a third-party node. To do so directly, you need to set up and maintain your own node on the network. This option is often chosen by those who are technically savvy and have the time and resources to maintain a node. The advantage of maintaining your own node is that you do not need to trust anyone, are in full control of the entire process, and can keep all the rewards generated by the node.
The other option is to delegate your coins to someone or an entity already running a node. A node that accumulates stakes from many individuals increases its chance of being selected to maintain the ledger. Of course, the node must share the reward it earns with all those who contribute to its stake.
Most protocols have a design that facilitates this form of staking natively, and that is known as delegated staking. In a few cases, while the protocol does not support delegated staking, third parties, especially exchanges like Coinbase, have designed layers on top of it that can take coins from multiple holders to stake through a single node or pool, increasing the chances of earning rewards.
In this case, the protocol deals with a single staking node. However, the layer manages coins from multiple stakers and shares the rewards based on their contribution. This layer at the top could also support restaking, where the same coins are staked on several networks, which increases the reward for the stakers.
There are cases where you stake without setting up a node or going through a third party. This is when you are a liquidity provider on a decentralized exchange or lending platform.
While with PoW, the incentive to act right is the reward and the punishment of not recovering the cost spent on energy, with PoS, the incentive is the reward and a loss of part of staked assets through slashing.
How easy it is to stake in this blockchain varies from blockchain to blockchain. Some have high minimum amounts that you can stake. For example, the least amount you can stake on Ethereum is 32 TH.
You may also like

Importance and benefits of staking
Staking benefits the protocol, the end users, and the stakers themselves.
Just like with the PoW, staking is a critical component of the governance structure of a blockchain or a decentralized application that runs on top of a blockchain. It regulates and manages the processing of transactions on networks without centralized authorities.
It is also more energy efficient, especially compared to Bitcoin’s Proof of Work consensus mechanism.
Meanwhile, the protocol’s end users benefit because their transactions are processed thanks to the staking process. For example, Ethereum users and all the applications that operate on the blockchain benefit from others staking their ETH to make the network functional.
Last but not least, the investors who run or contribute to the stake of nodes benefit by earning a return on their investment in the form of newly minted coins and the fees that network users pay. Staking is becoming a source of passive income, especially when delegated to others who manage the actual hardware resources.
Risks of Crypto Staking

You have to deal with a few risks when you choose to go into staking. The following are some of them:
Loss to slashing
While you may always try to play by the rules, the network might consider the activities of the node through which you are staking inappropriate. This can lead to you losing your investment through what is known as slashing.
Market volatility
It is always a possibility that the price of the asset you are staking can drop significantly. You are exposed even more to this risk if you are staking on a protocol that locks the assets for a specified time. That also becomes a liquidity concern.
Fraud
In some aspects of staking, you may have to trust others and hope that they act appropriately. This is more common when you stake on centralized platforms such as exchanges. Sometimes, these third parties control your assets, which can lead to fraud.
Protocol vulnerabilities
Any protocol that you stake on is as secure as the effectiveness of the smart contract code that runs it. Sometimes, the code has bugs or develops technical vulnerabilities after it is launched. Hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities, leading to losses.
Popular networks for Staking
The networks on which you can stake can be put into the following categories:
Layer 1 Blockchains
Staking was first used on blockchain networks. Peercoin, launched in 2012, was the earliest known blockchain to implement proof of stake. Today, the most popular PoS blockchains include Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, and Polkadot. Ethereum was founded as a PoW blockchain but switched to PoS in late 2022. It remains the most valuable PoS blockchain and the second most valuable overall.
Layer 2 Blockchains
These networks are built on top of existing blockchains. While they rely on the base chain, like Ethereum and Bitcoin, for security, they have their own consensus mechanism, and most are designed to use the proof-of-stake protocol.
The Ethereum blockchain hosts most blockchain L2s, including Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, Base, and BNB Chain. A few L2s have recently been launched on the Bitcoin network. While Bitcoin uses Proof of Work, almost all Bitcoin L2s use staking as part of their consensus protocol. The Bitcoin L2s include Stacks, Rootstock, Build on Bitcoin (BoB), and Merlin Chain.
Liquid Staking platforms
These decentralized networks governed as DAOs facilitate investors to stake but have access to their value to use elsewhere. It is a solution to the problem of having assets locked while staked. When you stake through these protocols, you receive a token that you can lend, use as collateral, or even restake. The list of liquid staking platforms includes Jito, Lido, Rocket Pool, and mETH Protocol.
Restaking platforms
These decentralized platforms are created to help you stake the same tokens simultaneously on several networks from a single user interface. The list of restaking platforms includes EigenLayer, Babylon, Symbiotic, and Renzo.
Decentralized exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are smart contract applications on the blockchain that help users swap between crypto assets. Staking on such an application involves actual staking as well as providing liquidity. When you stake on a DEX, you provide liquidity and, in return, receive a share of the fees users pay. The most popular DEXs to invest in include UniSwap, PanCakeSwap, Raydium, and Balancer.
You may also like

Lending platforms
These are similar to DEX in many ways. You provide liquidity that others can borrow, and in return, you share the fees and interest they pay. The most popular DeFi lending platforms where you can invest your assets include Aave, JustLend, and Compound Finance.
The Future of Crypto Staking
Proof of Stake continues to grow in popularity, especially given its environmental friendliness. The new blockchain and layer 2 platforms that are being created are more likely to use this form of consensus mechanism.
Also, DeFi is experiencing growth, and more financial services are becoming available through decentralized applications, which will drive further demand for staking. Meanwhile, DeFi is coming onto the Bitcoin blockchain through its own L2s. Most of these layers are more likely to use staking. All these create great potential and opportunities to invest and get great returns, mostly passively.
FAQ
When you stake your crypto, you don't give up ownership. The assets are still in your wallet, and the private keys are in your possession. When you stake, you signal to the network to consider your assets part of the stake of a particular node. In some protocols, you can't move the assets to a different wallet during the staking period. The only way you can lose your assets is through slashing if the node acts dishonestly.
That depends on the network or dApp on which you are staking. For example, staking on Ethereum requires a minimum of 32 ETH. However, you could stake even a smaller amount through third-party platforms.
There are two ways that your crypto can grow while it is staked. The first is through the rewards that you receive for staking. The second growth happens when the market is bullish. If you staked your ETH when the prize was $3000, and the prize is $3500 when you choose to unstake, your worth is up.
Generally, yes. By staking, you still retain ownership while earning rewards. Of course, other factors come into consideration, such as whether you are tech-savvy enough to securely stake your assets and access them in case you need them and the staking period has not elapsed.
Generally, no. You can't sell staked crypto. You will either unstake them first or wait for the staking period to elapse. However, there is the option of liquid staking on many networks. Liquid staking means using a platform that gives you tokens in return when you stake. You can use these tokens and lend them out.
Updated:
February 7, 2025
9 February, 2026
What Is a Trading Halt? Why Stocks Stop Trading and What It Means for You
A trading halt is when an exchange temporarily stops trading in a stock or, in rare cases, the entire market. It’s not a glitch and it’s not random. It’s a deliberate pause triggered when prices move too fast, critical information is about to be released, or regulators need time to step in. From the outside, […]



