What is OTC? Pros and Cons of Over-the-Counter Trading Instruments
Contents
The vast majority of assets are traded through centralized platforms like NYSE or NASDAQ where certain rules and requirements are mandatory for all sides. Meanwhile, there is a reverse side of the financial world – OTC (over-the-counter) deals that are executed directly between buyers and sellers, without third parties.
What is OTC Trading?
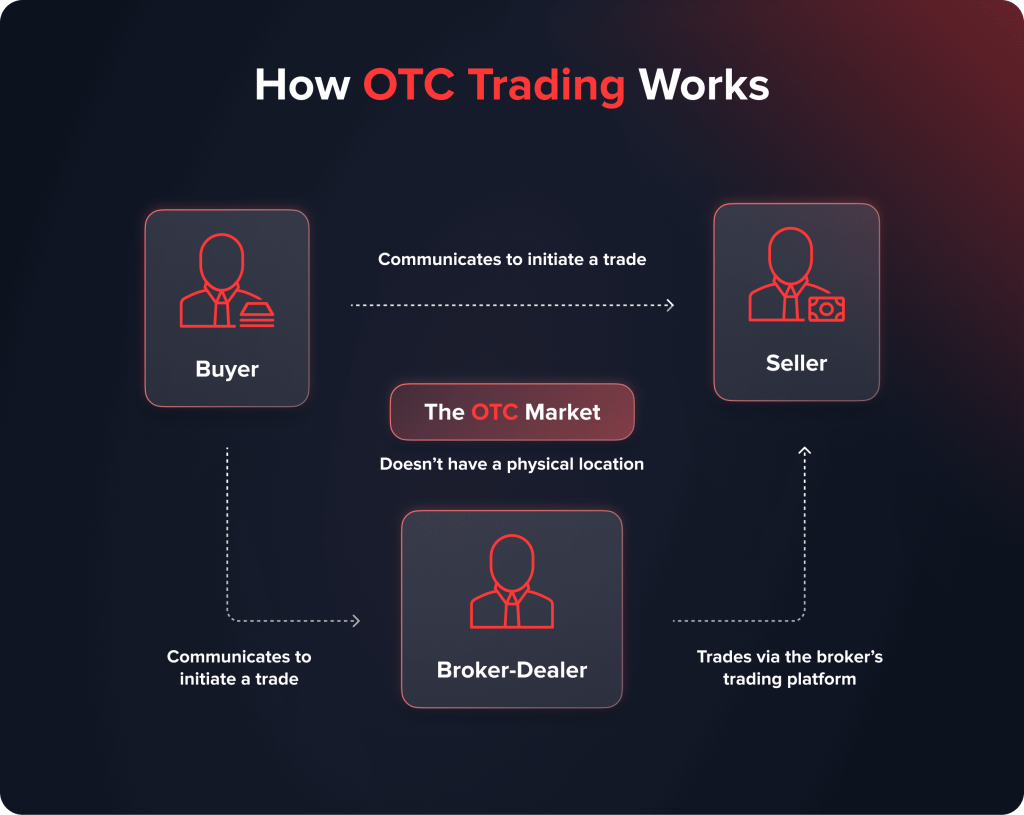
OTC trading is the process of buying and selling diverse financial instruments outside the official exchange platforms. Two parties interact directly with each other, without the influence of intermediaries.
The over-the-counter market has no physical location – all the transactions are made through a network of dealers. Such a system unlocks access to a much wider range of financial instruments.
The Key Differences Between OTC Trading and Exchange Trading
- Regulation aspects. All the deals that take place on a centralized exchange are strictly regulated by financial authorities. The over-the-counter market experiences less control.
- Centralization. As for the exchange trading, all the deals are recorded and standardized. When talking about OTC deals, buyers and sellers discuss individual conditions.
- Risks. Exchange transactions minimize default risks because of clearing houses, and over-the-counter instruments are not accompanied by such guarantees.
Over-the-counter instruments comprise stocks, derivatives, Forex, commercial papers, cryptocurrencies, and other assets. What are the peculiarities of the OTC market from the viewpoint of each category?
OTC Stocks
In simple words, the category of OTC stocks includes all the shares that are not listed on major exchanges. Investors are interested in such instruments due to several reasons. First and foremost, many promising startups do not enter exchanges because of high expenses and complexity; this is why investors fill their portfolios with shares with exceptionally high growth potential. On the other hand, some additional risks appear as well. For instance, OTC shares are usually marked by essential volatility and have different disclosure requirements.
When looking for over-the-counter stocks, the following markets are among the top-rated ones:
- OTCQX. This market is characterized by strict requirements towards financial reports. It welcomes investor-focused companies and has a stringent set of listing standards.
- OTCQB. The market also has strict requirements (but less stringent in comparison with OTCQB) towards listing to ensure investors that all the listed companies correspond to the transparency requirements and reporting standards.
- Pink Open Market. Requirements are not so strict which unlocks access to multiple small speculative companies.
OTC Derivatives
The market of OTC derivatives contains financial contracts with underlying assets. The role of an underlying asset can be performed by commodities, currencies, etc. Those contracts take the form of futures, options, swaps. Over-the-counter derivatives have no fixed rules and conditions – the two parties agree on rules and requirements on their own, without any middlemen. Flexibility is understood as the main advantage of OTC derivatives; meanwhile, credit risks appear – there is no extra layer of protection for such instruments.
The market of OTC derivative instruments steadily grows – analysts predict this sector to reach $25.8 billion by 2032 while the CAGR is 3.14%.
OTC Forex
The over-the-counter Forex trading means that all the deals are executed between Forex brokers and the network of banks. Exchanges do not participate in such trading mechanisms. Brokerage companies perform the role of intermediaries, issuers, and custodians of CFDs. The OTC Forex market is open around the clock. Furthermore, the market may offer some exotic currencies that are not available on traditional exchanges.
OTC Crypto
Cryptocurrencies traded in the over-the-counter mode do not enter trading platforms. Two parties meet each other through OTC desks and agree on prices and volumes. As such, digital assets are bought and sold directly without any middlemen. The two parties get the best conditions and complete anonymity.
As for other assets, bonds, commercial papers, and other instruments can be traded in the over-the-counter mode as well. Rules and requirements are the same – the two parties buy/sell assets without the interconnection with intermediaries.
Hence, OTC instruments are rather diverse. What are the main advantages and minuses of such deals?
Key Pros of OTC Markets
- Flexibility. The interaction between buyers and sellers makes it possible to discuss prices, volumes, and terms. Such a model helps two parties to find a compromise that suits both sides.
- Variety of instruments. The OTC market unlocks thousands of diverse assets including exotic ones. Many companies are not big enough to offer their shares through traditional exchanges; this is why the over-the-counter model turns out to be the best solution to find investors. As for investors, those meet a lot of promising assets available at attractive prices.
- Anonymity. In most cases OTC deals are anonymous – two sides discuss all the conditions on their own.
- Reduced trading costs. Traders and investors do not face tons of exchange fees and commissions as no third parties affect the process.
- No time limits. The OTC markets are available around the clock seven straight days, being not influenced by an exchange working days or hours.
Top Cons of OTC Markets
- Counterparty risks. In the exchange trading clearing houses guarantee that deal conditions will be fulfilled by both sides. As for over-the-counter instruments, one side may not fulfill its part of a deal.
- Low liquidity. Many instruments traded through OTC markets are low liquid which means an investor will not have an opportunity to sell such assets quickly at a fair price.
- Manipulation risks. While talking about assets that are not traded on traditional exchanges, high risks of manipulations appear.
You may also like

How to Enter the OTC Market? Useful Tips and Recommendations
Investors and traders cannot access over-the-counter instruments directly. They need to partner with an OTC trading provider. Here are some crucial criteria that mark a reliable provider:
- Regulation and licensing. Top-rated providers are licensed by reliable financial regulators.
- High rates. Look through the reviews to understand which companies are recommended by the community.
- Trading conditions and fees. Deal with providers that offer the best trading conditions and low fees.
- Wide range of financial instruments. The more assets are available through the OTC model, the better.

In most cases there are some top-players within each category: top-rated OTC Forex brokers, high-class OTC crypto desks, industry-leading platforms for OTC derivatives, etc. Never trust newcomer intermediaries who are accompanied with no reviews.
What are the Examples of OTC Deals?
Let’s dive deeper into the OTC trading process from the viewpoint of a company that wants to invest in exotic promising shares.
- For instance, a company AI Technologies is a promising startup that represents the Artificial Intelligence sector. Shares of AI Technologies are not listed on traditional exchanges.
- An institutional investor understands the high potential of the industry and wants to buy some shares of AI Technologies.
- An institutional investor applies to OTC brokers that unlock access to the OTC securities market.
- Several OTC brokers offer shares of AI Technologies and inform an institutional investor about the quotes. For instance, one broker is able to sell 10,000 shares at $3.20 per one share. Another broker offers 35,000 at $2.95 per share.
- An institutional investor compares all the available offerings and purchase shares from a broker with the best matching conditions.
- The trade is executed directly between two sides. Neither the fact of the transaction nor prices are disclosed publicly.
You may also like

What is the Future of OTC Markets?
Exchange trading is much safer and excludes most risks for investors; this is why such an option is frequently understood as the ground for the world financial systems. In fact, over-the-counter markets are much more important. OTC instruments are used by large investors, institutions, and funds which means the highest trading volumes take place outside traditional exchanges. The statistics show that OTC trading volumes continue to grow rapidly.
At present, over-the-counter instruments and intermediaries undergo the influence of technologies and updated regulation norms adapting to new trends and standards.
The OTC Market: Whether to Use or Not?
Over-the-counter trading instruments contain both pros and cons. The market is the best solution for large investors that are looking for exotic assets not listed on traditional platforms. Furthermore, OTC deals do not disclose prices and conditions publicly. On the other hand, this model is connected with higher risks for both buyers and sellers. From the viewpoint of institutional investors and other big players, OTC platforms are the best place for a deal. As for small retail investors, traditional exchanges are less risky and more transparent.
Updated:
December 19, 2024
9 February, 2026
What Is a Trading Halt? Why Stocks Stop Trading and What It Means for You
A trading halt is when an exchange temporarily stops trading in a stock or, in rare cases, the entire market. It’s not a glitch and it’s not random. It’s a deliberate pause triggered when prices move too fast, critical information is about to be released, or regulators need time to step in. From the outside, […]



